7 steps of knee revision surgery (2)
 Aug. 31, 2020
Aug. 31, 2020
7 steps of knee revision surgery (2)
Step 4: treatment of bone defect and recovery of joint line (operation difficulty)
There are two methods to deal with bone defect: allogeneic bone graft and metal block.
Allogeneic bone graft often has the disadvantage of bone resorption, so the metal block. is commonly used
Femoral metal block includes:
1. Distal Femoral Augment
The function is to restore the joint line and reduce the extension gap
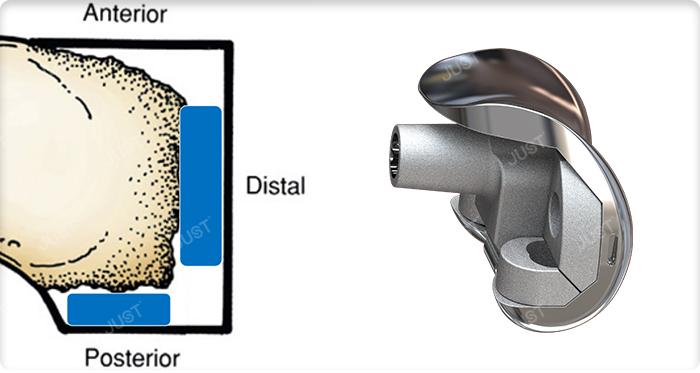
2. Posterior Femoral Augment
The function is to increase the stability of prosthesis, restore the correct rotation alignment, and reduce the flexion gap
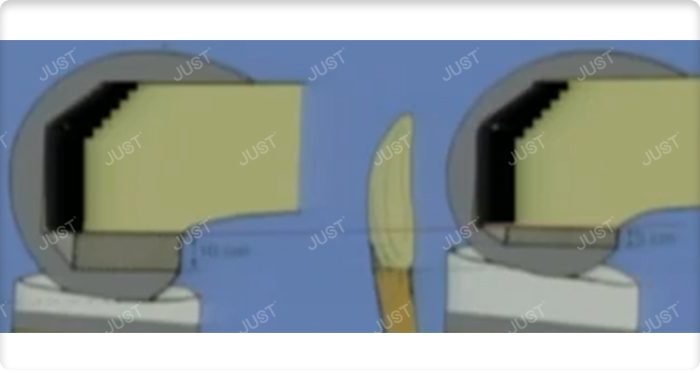
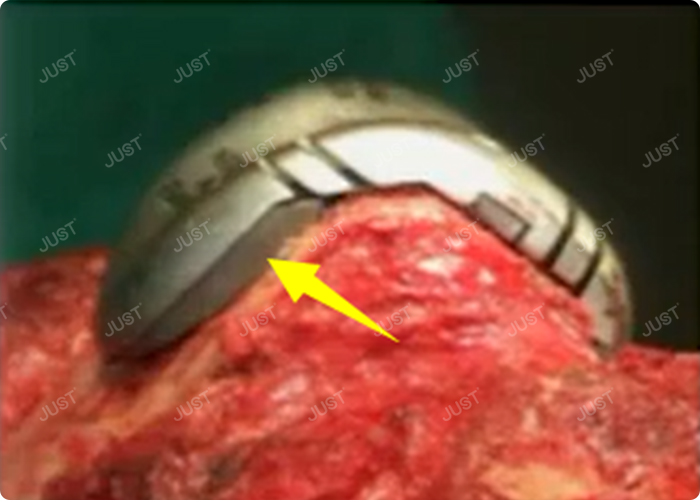
3. Anterior Femoral Augment
Rarely used, the function is to stabilize the prosthesis and ensure the correct position of the prosthesis in the medullary cavity
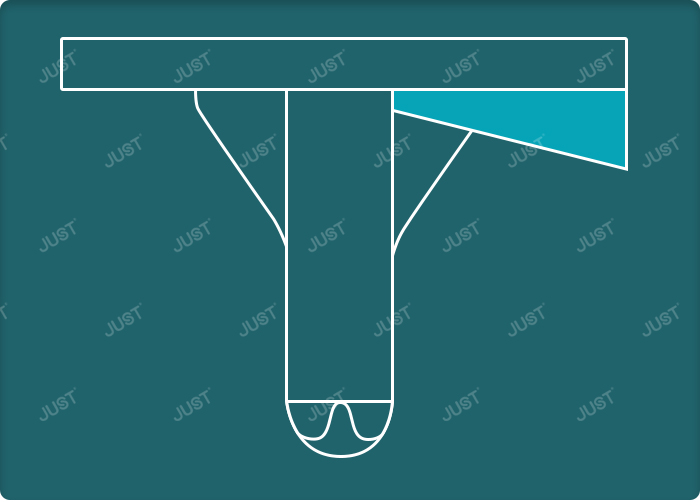
Tibial metal block includes:
1. Wedge block
The function is to replace the unilateral small bone defect (it can also be filled with screws and bone cement)
2. Rectangular block
The function of unilateral bone defect is to replace large bone defect
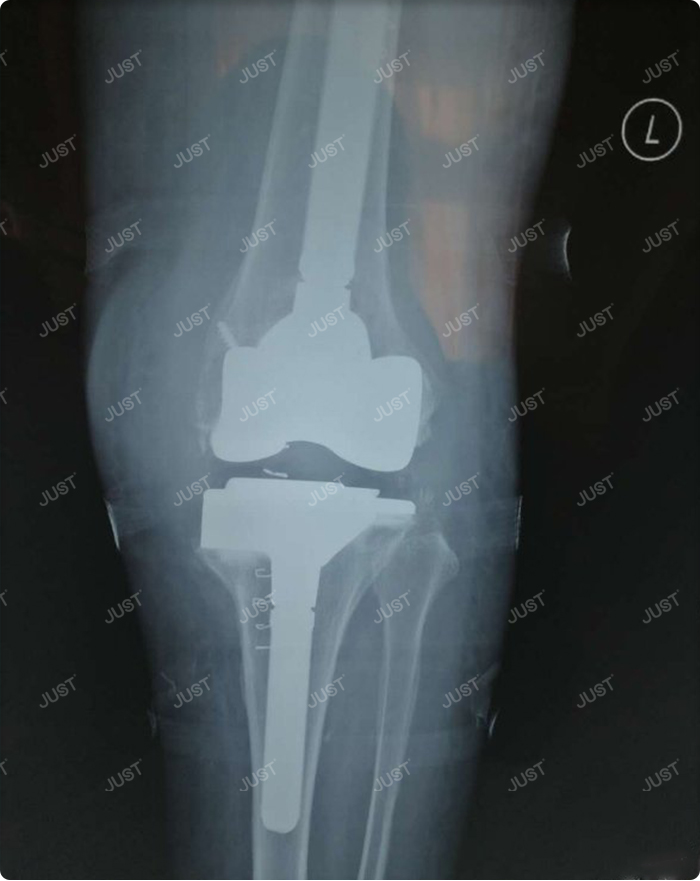
3. Bilateral block
The function is to balance the flexion and extension space, maintain the correct joint line, and the thickness of compensation platform cushion block is not enough
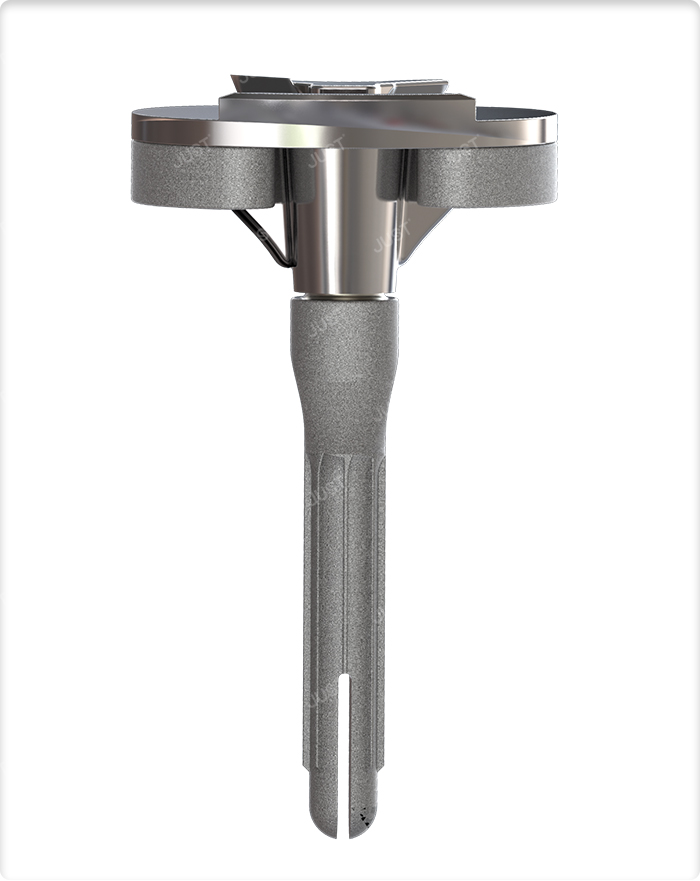

Especially serious bone defect, may use the center type cushion block, or TM cone, metaphyseal sleeve and so on.
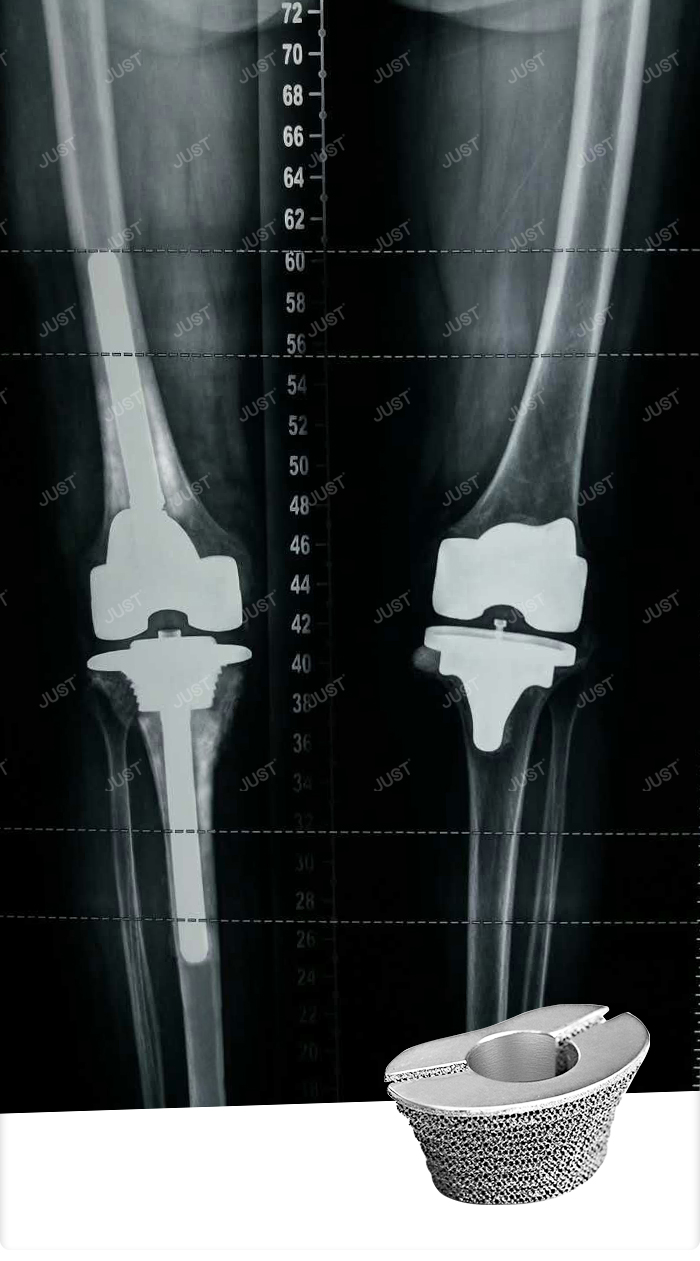
After the reconstruction of bone defect, the extension stem must be used to disperse the stress, protect the loose femoral condyle or allogeneic bone graft to help obtain the correct lower limb force line
The advantages of cemented extension stem are as follows

The advantages of cementless extension stem are as follows

More information about cement or cementless stem fixation, pls check this link: https://www.orthogate.org/videos/1702-cement-or-cementless-stem-fixation-which-is-best-in-tka













