Knowledge of revision knee joint (1)
 Aug. 10, 2020
Aug. 10, 2020
Knowledge of revision knee joint (1)
Today, let's talk about revision knee surgery.
The causes of failure of knee arthroplasty were as follows:
1, Infection (50% - 70%)
2, Aseptic loosening and instability
3, Wear and fracture
4, Joint stiffness
5, Patella problems
6, Periprosthetic fracture
7, Unexplained pain
Infection is the most common cause, how to deal with it?
Non revision treatment
Retention of prosthesis, debridement and replace the tibial bearing.
Within 3 months after operation, within 3 weeks after symptom.
Stable prosthesis, low toxicity infection, clear infection bacteria and sensitive antibiotics
Contraindications: high virulence drug-resistant bacteria infection, mixed infection, poor soft tissue coverage, sinus formation
Revision treatment
One stage operation
The advantages are one operation, fewer complications, shorter recovery period, lower cost and higher quality of life. Careful selection of indications and fine surgical techniques may be the reasons for the good effect of one-stage revision.
Prosthetic surgery techniques include: thorough debridement, irrigation, hand brushing and preoperative preparation, antibiotic bone cement, postoperative antibiotic use for more than 6 weeks.
Professor Cao Li of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University thinks: for the infection cases after artificial joint replacement, as long as the patients have good soft tissue conditions, no serious complications, dry surgical incision, no refractory pathogens (MRSA, pdr-pa, etc.), and CRP is lower than 60-90mg / dl for 5-6 days, it can be considered as safe.
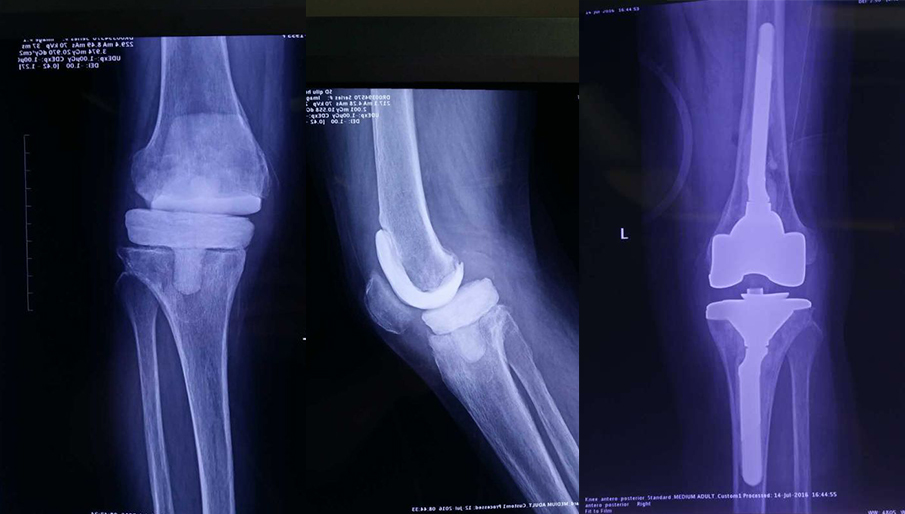
Prosthesis selection: mostly limited prosthesis(Fig.1)(Fig.2)
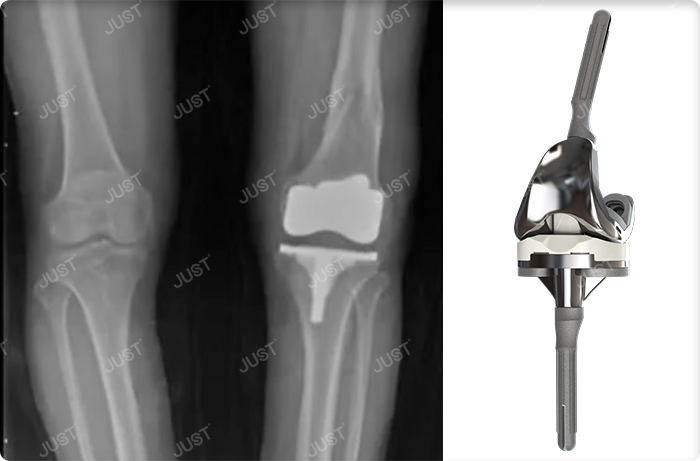
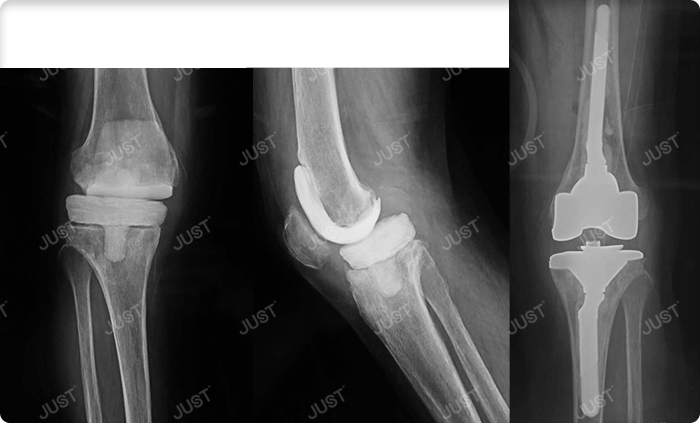
Second stage operation
Professor Zhou Yonggang of PLA General Hospital pointed out: Although the first stage of revision surgery has achieved good clinical results, the second stage revision is more effective in controlling infection and is still the gold standard for revision of joint replacement infection. It is necessary to pay attention to the importance of debridement and detection of pathogenic bacteria in the revision of infection, making antibiotic bone cement space occupying device, the use of antibiotics in the interval of second stage operation, and how to judge that the infection has been controlled, and when to carry out the second stage operation.
Prosthesis selection: the first operation, using antibiotic cement space occupying device to control infection. A restrictive prosthesis should be used.